Overview
Plastic pollution has emerged as one of the gravest environmental crises of our time, permeating every corner of the globe and impacting life on Earth in myriad ways. Despite its utility and economic value, the widespread use and disposal of plastic have led to significant ecological disruptions and health concerns, affecting ecosystems and communities worldwide.
From urban landscapes to remote oceanic gyres, the consequences of our plastic consumption are both far-reaching and enduring. Researchers have discovered microplastics embedded in the Arctic ice, indicating that plastic pollution affects even the most remote regions of the planet.
Startling Facts About Plastic Pollution

93% of Human Blood Samples Contain Microplastics
Microplastics have been detected in the bloodstreams of the vast majority of people tested, indicating widespread exposure.
99% of Seabirds Will Have Ingested Plastic by 2050
If plastic pollution progresses at the current rate, virtually all seabird species will be consuming plastic by mid-century.
The Great Pacific Garbage Patch: Twice the Size of Texas
The largest accumulation of ocean plastics in the world covers an area twice the size of Texas, trapping debris in a vast floating landfill.

1 Million Marine Animals Killed Annually by Plastic
Microplastics have been detected in the bloodstreams of the vast majority of people tested, indicating widespread exposure.
More Than 8 Million Tons of Plastic Dumped Annually
Each year, our oceans are burdened with over 8 million tons of plastic waste, equivalent to dumping the contents of one garbage truck into the ocean every minute.
Plastic Bag Found in the Mariana Trench: Earth’s Deepest Point
Scientists discovered a plastic bag at the bottom of the Mariana Trench, the deepest point of the world’s oceans, at nearly 36,000 feet below the surface.

Causes of Plastic Pollution
Intrinsic Properties of Plastic
Plastic is favored for its low cost, versatility, and durability, making it a preferred material in industries such as packaging, construction, and automotive.
Economic Incentives
The economic benefits of plastic, particularly disposable types, stem from their lower production costs compared to more sustainable alternatives. This cost-effectiveness perpetuates a cycle of mass production and wasteful disposal.
Waste Management Inefficiencies
Inadequate waste management systems, particularly in developing countries, struggle to cope with the escalating volumes of plastic waste, leading to significant environmental pollution.
Regulatory Gaps
The lack of stringent environmental regulations in many regions allows unchecked plastic production and disposal, exacerbating pollution and environmental harm.
Sources of Plastic Pollution
Plastic pollution originates from a wide array of sources, ranging from industrial activities to consumer products. Understanding the primary types of plastic pollutants and the countries where they are most prevalent is crucial for addressing this global issue effectively.
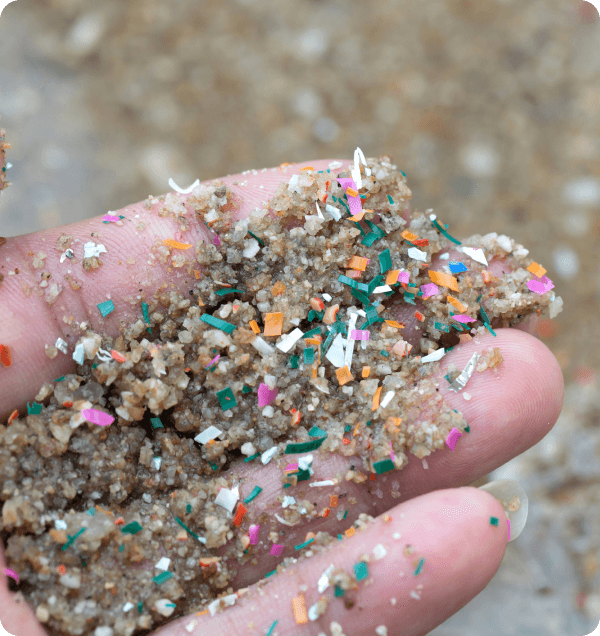
Types of Plastic Pollutants
- Single-Use Plastics Items like plastic bags, straws, coffee stirrers, soda and water bottles, and most food packaging are designed to be used once and then discarded. These account for a significant portion of the plastic waste that ends up in the environment.
- Microplastics These are small plastic pieces less than five millimeters long which can be harmful to our ocean and aquatic life. Microplastics come from a variety of sources, including from larger plastic debris that degrades into smaller and smaller pieces. In addition, microbeads, a specific type of microplastic, are very tiny pieces of manufactured polyethylene plastic that are added to health and beauty products, like some cleansers and toothpastes.
- Industrial Plastics Used in construction, agriculture, and manufacturing, these include large sheets, films, and pre-production plastics like nurdles (plastic pellets used to make other plastic products).
Countries Contributing to Plastic Pollution
While plastic pollution is a global issue, certain countries produce a disproportionately high amount of plastic waste due to various factors such as consumption patterns, waste management infrastructure, and industrial activities.

United States
As one of the largest producers of plastic waste, the U.S. generates large quantities of plastic, particularly single-use and packaging materials. Despite having advanced waste management systems, a significant amount of waste does not get recycled.

China
Previously the world’s largest importer of recyclable plastic, China has significant internal plastic waste issues exacerbated by rapid industrial growth and consumer market expansion.

India
High population density and rapid urbanization have led to increasing plastic consumption and waste, much of which is managed inadequately and ends up polluting both land and marine environments.

Southeast Asian Countries
Nations like Indonesia, the Philippines, and Vietnam face significant challenges due to high usage rates of single-use plastics combined with inadequate waste management and recycling infrastructures.
Understanding these sources and their global distribution helps in framing policies and strategies aimed at reducing the footprint of plastic waste. Enhanced international cooperation and stringent local measures are critical to managing the production and disposal of plastics more sustainably.
Snapshot of Plastic Pollution Issue
- How much plastic is produced per year: Over 380 million tons globally
- Percent That is Single Use: Approx. 50%
- Bottles Purchased Per Minute: Over one million (globally)
- Product Usage Lifespan: From a few minutes (e.g., plastic bags) to several months (e.g., disposable razors)
- Recycling Rate: Less than 10%
- Where does plastic waste go: Most ends up in landfills or oceans
- Environmental Impact: Unrecycled plastics often become microplastics, contaminating even remote terrestrial and marine habitats
- How Long Plastic Persists in Environment: Hundreds of years

Impact of Plastic Pollution

Plastic's Impact on the Environment & Natural Resources
Production and Pollution
Plastic production relies heavily on petroleum, consuming large amounts of energy and significantly increasing global carbon emissions. This process emits pollutants that degrade air quality and contribute to climate change.
Durability and Degradation
Plastic’s durability means it does not break down easily, allowing waste to persist in the environment for centuries. This resistance to degradation turns problematic when plastics accumulate in natural settings.
Contamination of Natural Resources
Once discarded, plastics contaminate soil and waterways, leaching harmful chemicals like bisphenol A (BPA) and phthalates. These substances disrupt ecosystems and affect critical resources, including water bodies that provide drinking water to millions.

Impact of Microplastics on Human Health
Presence in Human Tissues
Microplastics have been detected in various human tissues, including placentas, raising concerns about potential health risks to both fetuses and adults. These particles are known to carry carcinogens and endocrine disruptors that can enter the body through ingestion or inhalation, posing significant health risks.
Types of Health Risks
Associated health issues include hormonal imbalances, developmental disorders, and a heightened risk of chronic diseases such as cancer.
Accumulation and Interaction
Microplastics can accumulate within the body and interact with human tissues, a phenomenon that is concerning and still under extensive scientific investigation.

Wildlife at Risk from Plastic Pollution
Deadly Hazards for Wildlife
Plastic pollution causes significant fatalities among wildlife, with estimates suggesting that over one million seabirds and 100,000 marine mammals die each year due to plastic debris.
Ingestion and its Consequences
Marine animals, including turtles, seabirds, and whales, often mistake plastic waste for food, leading to ingestion. This can result in severe intestinal blockages, starvation, and poisoning from the chemicals in plastics. The resemblance of brightly colored plastics to natural prey further aggravates this issue, leading to widespread ingestion and contamination.
Ecosystem Disruption
Beyond immediate physical harm, plastic entanglement severely restricts animal movement, reduces reproductive success, and increases susceptibility to predators. This widespread contamination disrupts entire ecosystems.

Solutions to Plastic Pollution
Efforts to combat plastic pollution are diverse, involving numerous stakeholders each playing a crucial role in addressing the issue.

Governments
Governments are enacting legislation to curb the use of single-use plastics and enhance recycling efforts. For instance, many cities have banned plastic bags, and countries like India are aiming to eliminate single-use plastics by 2022.

NGOs
Non-governmental Organizations (NGOs) like The Ocean Cleanup are at the forefront of developing innovative technologies to remove plastics from our oceans, demonstrating proactive approaches to marine pollution.

Corporations
Corporations face increasing pressure from consumers and regulatory bodies to reduce plastic usage and are committing to significant sustainability goals. These efforts are vital in driving industry-wide changes towards more sustainable practices.
![]() Innovations leading the way forward
Innovations leading the way forward
Innovations in the sector include the development of biodegradable plastics from natural materials such as plant fibers, which decompose more quickly and with fewer environmental repercussions.
Advances in chemical and enzymatic recycling are transforming the way plastics are reused, turning waste back into valuable raw materials without the extensive environmental footprint of traditional recycling methods.
What You Can Do to Help?

Deepen Your Understanding
Dive into these key areas where ocean acidification has profound effects, exploring how it intersects with global environmental challenges and what it means for our planet’s future.

Bioplastics and Sustainability: Hype or Hope?
Examine the benefits and challenges of bioplastics as an alternative to traditional petroleum-based plastics.

Innovative Recycling Solutions for Plastic Waste
Explore new and emerging technologies that are transforming plastic recycling processes.

Going Plastic-Free: Is It Possible to Survive?
How to go plastic free across all the areas of your life, starting with small steps.
Top Environmental Issues
Read up on the top environmental issues facing us today
and the reasons WHY adopting a more sustainable lifestyle is so important.












